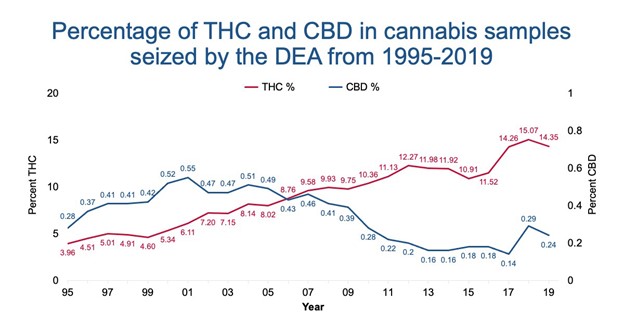
Weed. Ganja. Herb. Pot… whatever name you know it by, we know marijuana makes people feel “high,” but how? Why are certain types or strains of marijuana different in potency? And why does it even matter? The psychoactive chemical, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), is the main ingredient responsible for producing the euphoric “high” feeling that comes from using marijuana. Marijuana can have varying levels of THC, which can produce “stronger” or “weaker” strains. With no form of regulation, there is no way of knowing how much THC is in a particular batch of marijuana. So, why does it matter again? High levels of THC use have been associated with higher rates of addiction, anxiety, paranoia and even psychosis.
How Does THC Affect the Brain?
THC taps into the reward centers of our brain, altering our dopamine levels. Dopamine is associated with pleasurable sensations, along with learning, memory, motor system function, and more. Long-term marijuana use is associated with lower levels of dopamine. This can reduce motivation, pleasure and motivation. THC hijacks the reward system, and while a person is “high,” mundane activities seem exciting due to the reward centers being activated from using marijuana. Without THC, the reward centers do not activate the same way, even for previously rewarding activities.
Other Effects on the Brain
THC levels are at an all-time high in today’s marijuana, and data is just now starting to be analyzed for effects. We know that there are short-term and long-term effects from prolonged THC use. In the immediate aftermath, THC can cause:
- Short-term memory problems
- Anxiety
- Panic
- Hallucinations
- Lowered reaction time
- Increased heart rate (risk of heart attack)
- Increased risk of stroke
- Problems with coordination (impaired driving)
Other Sources of THC
Marijuana isn’t the only place THC is found. Vape cartridges, edible THC and synthetic marijuana can also contain THC. The same problem persists with these products as they do with the others… there’s no regulation or way of knowing how much THC is in any individual product. Even synthetic marijuana that claims to have “low or no” THC can still create cognitive impairments, plus lead to a failed drug test. The bottom line is simple: THC is a psychoactive chemical that alters your brain, leading to short-term and long-term issues. To avoid these issues, steering clear of THC and being drug-free is the way to be.
Sources:
DiLonardo, M. J. (n.d.). CBD vs. THC: Properties, benefits, risks, & legality. WebMD. Retrieved December 3, 2021, from https://www.webmd.com/pain-management/cbd-thc-difference
Holland, K. (2020, July 20). What’s the difference between CBD vs. THC? Healthline. Retrieved December 3, 2021, from https://www.healthline.com/health/cbd-vs-thc.
National Institute on Drug Abuse. (2021, April 13). How does marijuana produce its effects? National Institute on Drug Abuse. Retrieved December 3, 2021, from https://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/research-reports/marijuana/how-does-marijuana-produce-its-effects#:~:text=As%20a%20result%2C%20using%20marijuana,%2C%20coordination%2C%20and%20reaction%20time.
The science of marijuana: How THC affects the brain. Scholastic. (n.d.). Retrieved December 3, 2021, from http://headsup.scholastic.com/students/the-science-of-marijuana




Comments are closed.